Are you curious about your dog’s breed, health, or genetic traits?
Pet DNA testing has become a popular way for pet parents to find out more about their furry friends. Whether you are wondering about breed-specific traits or concerned about potential health risks, a DNA test can offer fascinating insights. You can learn more about your dog’s genetic makeup with an easy-to-use, reliable DNA test kit, and enhance your pet care journey. Let’s get into it.
What Is a Dog DNA Test?
Put simply, a dog DNA test allows you to uncover detailed information about your dog's breed, traits, and health. The test identifies genetic markers that reveal the breeds and lineages by analyzing a small sample of your dog's saliva or cheek cells.
Some DNA tests go even further, offering insights into each breed’s origins, behavioral traits, and physical attributes, helping you understand your dog’s unique personality and potential health risks.
History of Dog DNA Testing
Evolution and Advancements
The Human Genome Project completed the first full sequencing of the human genome in 2003. Just a year later, the complete genome of a Boxer dog named Tasha was successfully sequenced. Since then, dog genetic testing has advanced in leaps and bounds, and can identify more than 900 hereditary diseases and genetic predispositions in dogs, providing deeper insights into pet health.
A dog DNA test kit can enable pet owners to take a more proactive approach to their dogs' care, so much so that many breeding associations and veterinary groups now recommend genetic testing to reduce the risk of inherited diseases.
Initial Uses and Current Applications
Dog DNA testing was initially used for breed identification, helping pet owners learn more about their dog's lineage, but is now also used for identifying disease-causing genetic mutations, offering valuable insights into potential health risks.
How Dog DNA Testing Works
Sample Collection: Cheek Swab
Collecting a canine DNA sample is simple and can be done at home. A dog DNA test requires you to gently swab your pet's oral cavity to collect cells from their mouth, making DNA collection quick, easy, and non-invasive for your pet.
Laboratory Analysis
There could be different approaches to dog DNA analysis. For example, the Basepaws dog DNA test uses Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) technology for the most advanced and accurate dog DNA analysis, allowing us to provide highly detailed insights into your dog’s genetic makeup, from breed identification to potential health risks. This means that you can trust that you’re receiving the most reliable and comprehensive results, helping you make informed decisions for your pet’s health and well-being.
Interpretation of Results
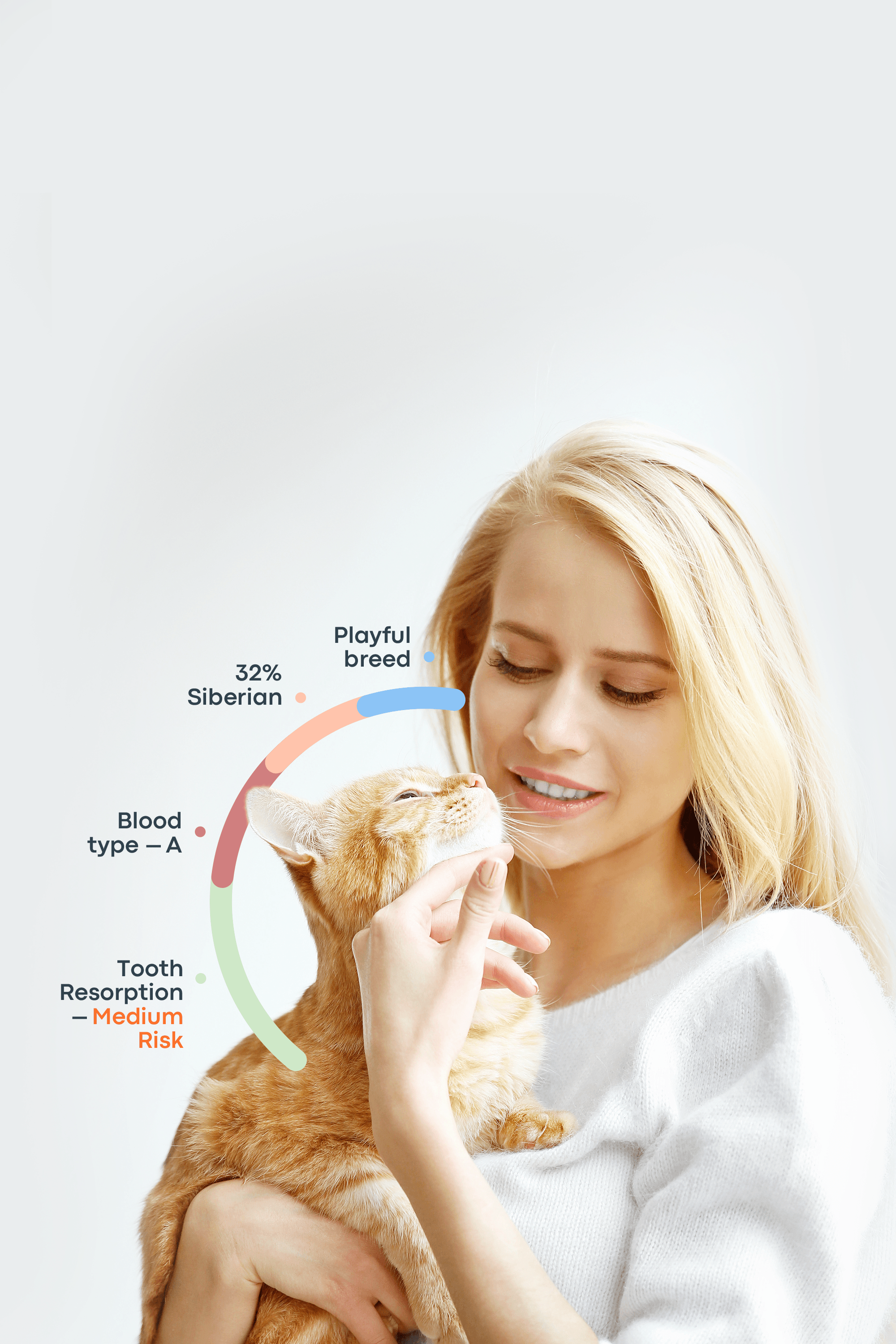
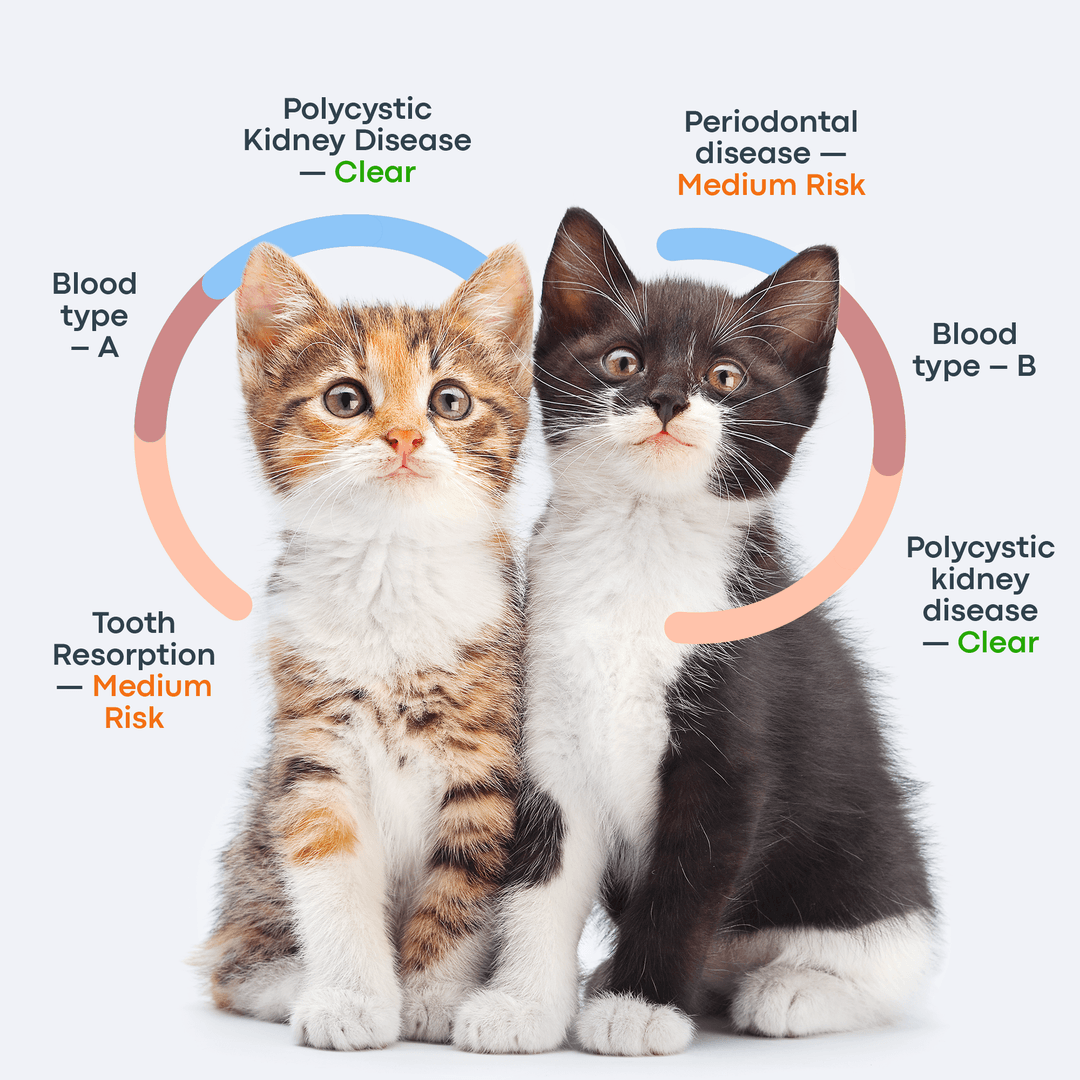
Dog DNA test results are typically categorized into different statuses: ‘Negative’ or ‘Clear’ means your pet doesn't carry the genetic mutation for a specific disorder, though environmental and lifestyle factors can still influence disease risk. ‘Carrier’ indicates your pet may pass the mutation to offspring without showing symptoms themselves.
For health related markers, you may see ‘At Risk’ and it means that your dog has inherited genetic markers associated with a particular health condition and may develop the disease, depending on the number of mutated copies and the specific inheritance pattern. Phrases like ‘Likely’ or ‘Likely to Have’ are generally used for trait markers, indicating your dog is positive for markers linked to specific physical traits and is likely to express them.
Result Category | Meaning | Implications |
Negative / Clear | No genetic mutation detected | Low risk, but environment may still play a role |
Carrier | One copy of the mutation, no symptoms | May pass condition to offspring |
At Risk | Inherited mutation(s) | Potential to develop condition |
Likely / Likely to Have | Associated with traits | Dog is likely to express certain traits |
Note: ‘Carrier’ status for traits or health risks inherited in an autosomal incompletely dominant manner may result in an intermediate phenotype. For example, a carrier of a mutation associated with shedding may show a moderate amount of shedding, compared to individuals with heavy or light shedding.
How Long Does a Dog DNA Test Take?
Average Processing Time
DNA testing for dogs takes time, with most results typically arriving in about four to six weeks, although the exact processing time can vary. Once the analysis is complete, your results may be delivered online, via mail, or sent directly to your veterinarian for review.
While the wait may feel long, this thorough genetic testing process ensures that you receive accurate and detailed information about your pet. Patience pays off in the form of valuable insights into your pet’s well-being.
Factors Influencing Result Timing
Like many tests, there could be a variety of factors affecting the timing of receiving your results. These factors may include the processing time at the lab, for example, or the complexity of the test, the sample quality, whether the test includes breed identification or health screening and so on.
Step-by-Step Process Timeline
From Sample Collection to Results
The process of dog DNA tests starts with a quick 5-10 second swab of your dog’s gums and teeth to collect a DNA sample. Be sure to follow the instructions carefully—mistakes in sample collection or shipping may affect the results.
Once collected, return the sample using the provided packaging. The lab will then purify your pet’s DNA and take care of the rest, and you can expect to receive your results in about 4-6 weeks.
Step | Description | Time Estimate |
1. Collect Sample | Swab dog’s mouth | 5–10 seconds |
2. Send Sample | Use prepaid return packaging | 1–5 days (shipping) |
3. DNA Extraction | In lab, isolate DNA from sample | 1–3 days |
4. Genetic Sequencing & Analysis | Identify markers | 2–3 weeks |
5. Results Delivered | Email, app, or vet | ~4–6 weeks from start |
What Happens in the Lab?
In the lab, the dog's DNA is extracted from a saliva sample. The DNA then undergoes a series of post-processing procedures to prepare it for sequencing. Experts will then analyze key genetic markers related to breed and potential health conditions, from which they will compile a report of the results detailing the dog's breed composition and any detected traits or health risks.
Conclusion
Dog DNA testing offers pet owners valuable insights, helping to ensure healthier breeding practices and reducing the likelihood of genetic issues in purebred puppies. It also informs your veterinarian of potential health risks, allowing you to make proactive care decisions for your pet. If your pet is at risk for an inherited disorder, discussing the results with your vet can help create a plan to proactively support your pet’s well-being.