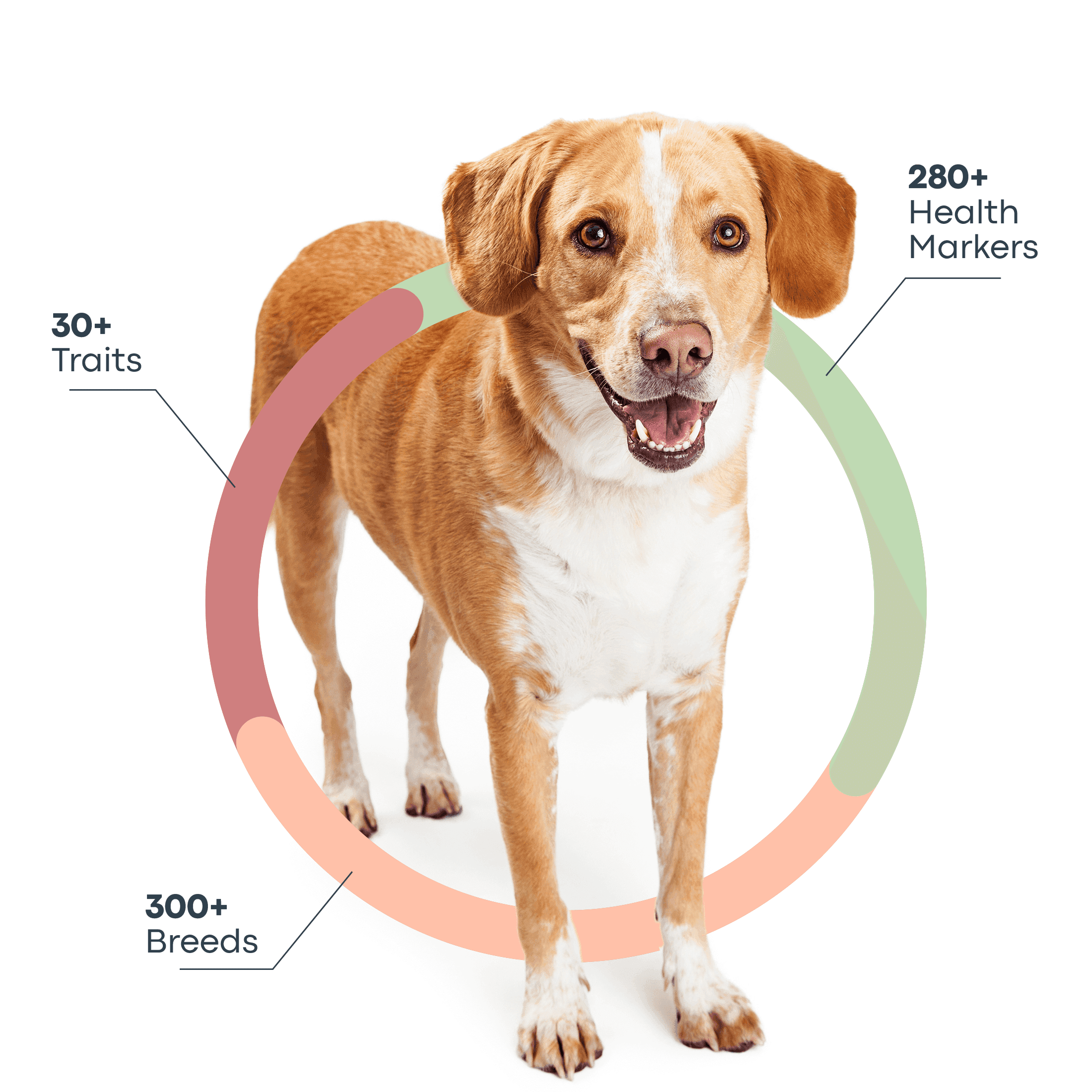
Breeds
Breeds
The following is a list of breeds, landraces, and free-breeding dogs Basepaws can identify.
What is a lineage? What does it mean to get a lineage result?
A canine genetic lineage is a group of individuals or entire breeds that descended from common ancestors predating modern breed formation. Often these lineages are associated with a ‘type’ of dog with a unique historical working role and associated behaviors (e.g., herding, scent hunting, etc.).
By categorizing complex ancestry by lineage in addition to breed, we can understand the ‘types’ of dogs contributing to your dog's unique genetic makeup and their associated health, behavioral, and aesthetic traits.
 Diseases
Diseases
The following is a list of genetic conditions we test for in dogs.
Cardiac disorders
Dermatologic disorders
- Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
- Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS)
- Hyperkeratosis, DSG1-related
- Hyperkeratosis, FAM83G-related
- Hyperkeratosis, KRT10-related
- Hypotrichosis
- Ichthyosis, PNPLA1-related
- Ichthyosis, SLC27A4-related
- Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevi (ILVEN)
- Junctional epidermolysis bullosa, LAMA3-related
- Junctional epidermolysis bullosa, LAMB3-related
- Lethal acrodermatitis
- Nasal parakeratosis
- X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (XHED)
Endocrine disorders
Gastrointestinal disorders
Hematologic disorders
- Bleeding disorder, P2RY12-related
- Canine Scott syndrome (CSS)
- Elliptocytosis
- Factor VII deficiency
- Factor XI deficiency
- Haemophilia A
- Haemophilia B
- Ligneous membranitis
- May-Hegglin anomaly
- Methemoglobinaemia
- Polycythemia
- Prekallikrein deficiency
- Thrombasthenia
- Thrombocytopaenia
- Thrombopathia
- Von Willebrand disease I
- Von Willebrand disease II
- Von Willebrand disease III
Immune disorders
- C3 deficiency
- Leukocyte adhesion deficiency, type I
- Leukocyte adhesion deficiency, type III
- Leukodystrophy, TSEN54-related
- Severe combined immunodeficiency disease, DNA-PKcs-related
- Severe combined immunodeficiency disease, RAG1-related
- Severe combined immunodeficiency disease, X-linked
- Trapped Neutrophil Syndrome
Metabolic disorders
- Beta-mannosidosis
- Ciliary dyskinesia, CCDC39-related
- Ciliary dyskinesia, NME5-related
- Erythrocytic pyruvate kinase (PK) deficiency
- Exercise induced metabolic myopathy
- Gangliosidosis, GM1
- Gangliosidosis, GM2, type I
- Gangliosidosis, GM2, type II
- Glycogen storage disease, type IA
- Glycogen storage disease, type II
- Glycogen storage disease, type IIIA
- Glycogen storage disease, type VII
- Hypocatalasia (Acatalasemia)
- Menkes disease
- Mucopolysaccharidosis IIIA
- Mucopolysaccharidosis VI
- Mucopolysaccharidosis VII
- Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, ARSG-related
- Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, ATP13A2-related
- Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, CLN5-related
- Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, CLN6-related
- Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, CLN8-related
- Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, MFSD8-related
- Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, PPT1-related
- Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, TPP1-related
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency
- Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency
- Wilson's disease, ATP7B-related
- Xanthinuria, type I
- Xanthinuria, type II
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
- Australian Labradoodle dystrophinopathy
- Centronuclear myopathy
- Chondrodysplasia, FGF4-related
- Chondrodysplasia, ITGA10-related
- Craniomandibular osteopathy
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, classic-like type
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Dermatosparaxis type
- Exercise-induced collapse syndrome (EIC)
- Hypophosphatasia
- Inflammatory myopathy
- Inherited Myopathy of Great Danes (IMGD)
- Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 2F
- Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type R3
- Malignant hyperthermia
- Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy
- Muscular dystrophy, COL6A3-related
- Muscular hypertrophy (double muscling)
- Musladin-Lueke syndrome
- Myotonia
- Myotubular myopathy
- Oculoskeletal dysplasia, COL9A3-related
- Osteogenesis imperfecta, COL1A1-related
- Osteogenesis imperfecta, COL1A2-related
- Osteogenesis imperfecta, SERPINH1-related
- Progressive retinal atrophy, RHO-related
- Renal cystadenocarcinoma and nodular dermatofibrosis
- Skeletal dysplasia 2 (SD2)
- Spondylocostal dysostosis
- Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD)
Neurologic disorders
- Alexander disease
- Bandera's neonatal ataxia (BNAt)
- Benign familial juvenile epilepsy (BFJE)
- Cerebellar ataxia, KCNIP4-related
- Cerebellar ataxia, RAB24-related
- Cerebellar ataxia, SEL1L-related
- Congenital myasthenic syndrome, CHAT-related
- Congenital myasthenic syndrome, CHRNE-related
- Congenital myasthenic syndrome, COLQ-related
- Dandy-Walker-like malformation (cerebellar hypoplasia)
- Degenerative myelopathy
- Generalized myoclonic epilepsy with photosensitivity
- Hypomyelination
- Juvenile-onset neuroaxonal dystrophy, TECPR2-related
- Krabbe disease
- L-2-hydroxyglutaricacidemia
- Laryngeal paralysis and polyneuropathy
- Leigh-like subacute necrotizing encephalopathy (SNE)
- Mitochondrial neurodegenerative disease with epileptic encephalopathy
- Multiple system degeneration
- Narcolepsy
- Neonatal encephalopathy with seizures
- Neuroaxonal dystrophy, PLA2G6-related
- Neuroaxonal dystrophy, VPS11-related
- Neurodegenerative vacuolar storage disease
- Neurological defects, MYO5A-related
- Pelizaeus-Merzbacker disease (shaking pup disease)
- Polyneuropathy, ARHGEF10-related
- Polyneuropathy, GJA9-related
- Polyneuropathy, NDRG1-related
- Polyneuropathy, RAB3GAP1-related
- Sensory neuropathy
- Spinocerebellar ataxia, CAPN1-related
- Spinocerebellar ataxia, KCNJ10-related
- Spinocerebellar ataxia, SCN8A-related
- Spinocerebellar ataxia, SPTBN2-related
- Spongy degeneration with cerebellar ataxia (SDCA)
- Spongy degeneration with cerebellar ataxia 1 (SDCA1)
Ophthalmologic disorders
- Achromatopsia, CNGA3-related
- Achromatopsia, CNGB3-related
- Cone-rod dystrophy 2 (crd2)
- Cone-rod dystrophy 4 (crd4)
- Congenital eye malformation
- Congenital keratoconjunctivitis sicca and ichthyosiform dermatosis (CKCSID)
- Congenital stationary night blindness
- Early retinal degeneration (erd)
- Goniodysgenesis and early-onset glaucoma
- Lens luxation
- Multifocal retinopathy 1
- Multifocal retinopathy 2
- Multifocal retinopathy 3
- Primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG), ADAMTS10-related
- Primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG), primary lens luxation (PLL), or both
- Progressive retinal atrophy, BBS4-related
- Progressive retinal atrophy, CCDC66-related
- Progressive retinal atrophy, CNGA1-related
- Progressive Retinal Atrophy, CNGB1-related
- Progressive Retinal Atrophy, HIVEP3-related
- Progressive Retinal Atrophy, IFT122-related
- Progressive Retinal Atrophy, NECAP1-related
- Progressive Retinal Atrophy, SAG-related
- Progressive retinal atrophy, SLC4A3-related
- Progressive retinal atrophy, TTC8-related
- Progressive retinal atrophy, X-linked, type 1
- Progressive retinal atrophy, X-linked, type 2
- Progressive rod-cone degeneration
- Rod-cone dysplasia 1 (rcd1), PDE6B-related
- Rod-cone dysplasia 3 (rcd3)
- Stargardt disease 1
- X-linked retinal dysplasia
Other systems disorders
- Amelogenesis imperfecta, ENAM-related
- Deafness, bilateral, and vestibular dysfunction
- Deafness, unilateral and vestibular dysfunction
- Decreased litter size
- Dental hypomineralization
- Disorder of sexual development, SRY-related
- Leukoencephalomyelopathy
- Multiple Drug Sensitivity (MDR1)
- Non-syndromic hearing loss
- Periodic Fever Syndrome
- Persistent Müllerian duct syndrome
Renal/Urinary disorders
Respiratory disorders
 Traits
Traits
The following is a list of genetic traits we test for in dogs.